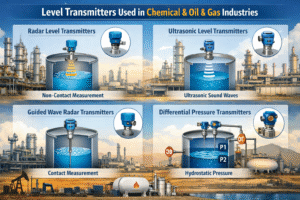
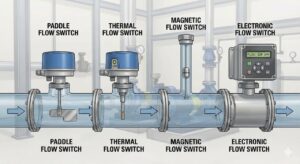
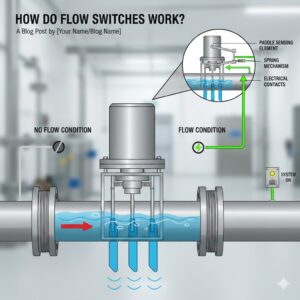
Pressure transmitters are essential instruments in industries like oil & gas, pharmaceuticals, water treatment, and manufacturing.
They convert pressure measurements into electrical signals that control and monitor critical processes.
However, like any sensitive device, pressure transmitters can develop issues over time due to harsh environments, wear and tear, or improper handling.
In this blog, we’ll explore the most common pressure transmitter problems, their causes, and practical solutions to help you keep your systems running smoothly.
- Pressure Transmitter Troubleshooting
When a pressure transmitter suddenly stops giving accurate readings, proper troubleshooting becomes the first step. Many times, the issue is not with the device itself but with wiring, power supply, or signal interference.
Common causes:
- Loose or damaged wiring
- Unstable power supply
- Poor grounding
Solutions:
- Check and tighten all wiring connections
- Verify voltage levels using a multimeter
- Ensure proper earthing to prevent electrical noise
Regular troubleshooting helps identify minor problems before they become serious faults.
- Pressure Transmitter Issues
Pressure transmitter issues often show up as fluctuating readings, delayed response, or complete signal loss. These problems may appear gradually or suddenly.
Typical reasons:
- Moisture or dust entering the transmitter housing
- Clogged impulse lines
- Aging electronic components
Solutions:
- Inspect and clean impulse lines regularly
- Replace worn-out seals and gaskets
- Keep the housing properly sealed to prevent contamination
Preventive inspection plays a major role in avoiding repeated transmitter issues.
- Common Pressure Sensor Problems
Pressure sensor problems directly affect the accuracy of the pressure transmitter. Sensors are delicate and sensitive to environmental conditions.
Common problems include:
- Sensor drift over time
- Damage due to overpressure
- Corrosion from aggressive chemicals
Solutions:
- Use pressure transmitters with suitable pressure ratings
- Install protective diaphragms and seals where needed
- Replace sensors that show excessive drift or physical damage
Choosing the right sensor for the application reduces long-term failures.
- Pressure Transmitter Faults
Pressure transmitter faults can be electrical or mechanical in nature. Electrical faults are more common in industrial environments due to power fluctuations.
Causes:
- Short circuits
- Blown internal fuses
- Component failure on circuit boards
Solutions:
- Inspect internal circuitry if you’re trained to do so
- Replace damaged components or the entire transmitter if necessary
- Install surge protectors to prevent voltage spikes
Timely fault detection ensures process safety and avoids costly downtime.
- Pressure Transmitter Errors
Pressure transmitter errors are often seen in the form of incorrect digital displays or error codes in control systems.
Reasons for errors:
- Incorrect parameter settings
- Communication issues with PLC or DCS systems
- Software glitches
Solutions:
- Reconfigure the transmitter using the manufacturer’s software or handheld communicator
- Check communication protocols and cabling
- Update firmware where supported
Software-level maintenance is just as important as hardware checks.
- Pressure Transmitter Repair
In some cases, replacing the entire transmitter may not be necessary, and a simple repair can restore its functionality.
Situations where repair is possible:
- Damaged terminal blocks
- Worn-out connectors
- Minor circuit damage
Repair tips:
- Always isolate power before opening the transmitter
- Use original spare parts when available
- Perform functional testing after repair
Where repairs are complex, it’s safer to consult certified service technicians.
- Pressure Transmitter Failure Causes
Understanding pressure transmitter failure causes can help prevent future breakdowns.
Common causes include:
- Excessive vibration
- Extreme temperature conditions
- Exposure to corrosive or explosive atmospheres
Solutions:
- Use vibration-resistant mounting brackets
- Install temperature shields or cooling accessories
- Select transmitters with appropriate material coatings
Designing the installation environment properly greatly extends device lifespan.
- Pressure Transmitter Working Issues
When pressure transmitters experience working issues, performance becomes inconsistent and unreliable.
Signs of working issues:
- Slow response time
- Intermittent signal output
- Random spikes in readings
Solutions:
- Check for blockages in pressure ports
- Test signal output with a standard calibrator
- Replace aging transmitters that no longer meet accuracy requirements
Consistent monitoring helps catch these issues early.
- Pressure Transmitter Maintenance
Good pressure transmitter maintenance is the backbone of reliable operations. Without a proper maintenance routine, even high-quality transmitters can fail.
Best maintenance practices:
- Regular visual inspections
- Cleaning of pressure ports and impulse lines
- Periodic tightening of electrical connections
Proactive maintenance reduces emergency repairs and extends equipment life.
- Pressure Transmitter Calibration Problems
Calibration problems are one of the most common challenges faced by technicians. Incorrect calibration leads to inaccurate pressure readings and poor process control.
Also read : Benefits of Using Wireless Pressure Transmitters
Typical calibration problems:
- Zero shift
- Span errors
- Calibration done under incorrect environmental conditions
Solutions:
- Perform calibration using certified instruments
- Follow manufacturer-recommended calibration intervals
- Always calibrate under stable temperature and pressure conditions
Accurate calibration ensures reliable and trustworthy measurements.
Conclusion
Pressure transmitters are critical instruments that demand proper care and attention. Most problems arise from environmental exposure, lack of maintenance, or improper installation. By understanding common pressure transmitter faults, errors, and failure causes, engineers and technicians can implement preventive strategies to maintain system reliability.
Regular troubleshooting, timely repair, preventive maintenance, and proper calibration are the keys to keeping pressure transmitters functioning accurately and efficiently in any industrial setting.